P/O Criteria (PO09_PO_PC)
The P/O Criteria (ibis_po_pc.po09) table allows you to define the purchasing criteria that are assigned to supplier product records in P/O Purchasing Information (ibis_popi.po13). Purchasing criteria are used to determine when a product should be reordered. Reorder quantities (ROQs) are calculated by the system to determine the quantity to be ordered.The following list defines every field available in the P/O Criteria (po_pc) table in alphabetical order:
- Company - the company field is available when you create a new PO criteria record. The company defaults to the company assigned to your user id in the Session Parameters view. You can change the default company during the criteria creation process only. Once the record is created, the company to which the record is associated displays in the General section (at the top of the view).
- Created By - displays the name of the user who created the record you are viewing or maintaining. May not be overridden.
- Created On - displays the date on which the record that you are creating or maintaining was created. May not be overridden. May also represent the creation date of the records you are attempting to retrieve.
- Description - the description of the purchase criteria code. The description can be a maximum of 30 alpha-numeric characters in length.
- Maximum Factor - the factor to be used by the recalculation routines for this purchase criteria code to obtain system-calculated maximums. The default value is 1.
- Note: The maximum factor can also be applied on a supplier-by-supplier basis if the max. factor is defined in the Suppliers (ibis_pos.po11) table. In this case, all products for a supplier will use the supplier's max. factor, if it is greater than zero.
- Min. Mos. for Max Calculation - the number of months that a product must be on file in order for the recalculation routines (Purchasing, Forecast and Leadtime Recalculation (ibis_po25) and Purchasing Recalculation Edit (PO27)) to recalculate the purchasing criteria and forecast automatically. You can enter a maximum of 24 months in this field. The default value for this field is 6 months.
-
Note: If a product does not meet the minimum months for maximum calculation value specified here (meaning that there isn't enough demand history), then the purchasing criteria for the product will not be recalculated. These values (minimum, maximum, reorder point, reorder quantity and line point) must be maintained manually until enough history is accumulated. Monthly forecast will be recalculated but is calculated as a straight average of total demand to-date divided by no. of months active (including or excluding the current month's demand).
- Modification Counter - this field is not maintainable. The date and time the record was last modified.
- Modified By - this field is not maintainable. The user or system process that last modified the record.
- Modified On - this field is not maintainable. The date on which the record was last modified.
- Purchase Criteria Code
- the purchase criteria code. The code can be a maximum of 2 alpha-numeric characters in length.
- Re-calc. Max. - the following options are available: Yes (default) and No.
- A value of Yes indicates that the recalculation programs (ibis_po25/ibis_po27) calculate and define the maximum stock level for products, and automatically update the Products (ibis_ici1) table.
- A value of No indicates that the maximums must be set manually in the Products (ibis_ici1) table or all products.
- A value of Yes indicates that the recalculation programs (ibis_po25/ibis_po27) calculate and define the maximum stock level for products, and automatically update the Products (ibis_ici1) table.
- ROQ Calculation Method - controls how the purchasing system generates the suggested quantity of a product to order each time the product is in a position to be reordered.
There are four methods of calculating the ROQ (Reorder Quantity):
- Manually set ROQ amount - the amount to be reordered is manually set for the product in the Porducts (ibis_ici1) table. This amount may only be reset manually.
- Order Up To Maximum - maximums are calculated in one of two ways, depending on whether the supplier is reviewed cyclically or on an 'as required' basis:
- If reviewed cyclically, maximums are calculated as:
Maximum = Line Point + Forecast x Lead-time x Maximum Factor
The difference in quantity between available units and maximum units is the reorder value, providing the inventory level is below the line point. When available stock drops below the line point, and when P/O Preliminary Generation (ibis_po23) runs, a preliminary PO is generated to bring stock levels back to the maximum.
Note: The line point and the maximum values are stored in the Products (ibis_ici1) table. These values are updated on an on-going basis through the Purchasing, Forecast and Leadtime Recalculation (ibis_po25) process.
Note: P/O Preliminary Generation (ibis_PO23) generates the reorder values for any supplier using this method of calculating ROQ.
- If reviewed on an 'as required' basis (i.e. 'Review Cycle ROQ' is not selected), maximums are calculated as:
Maximum = Reorder Point + Forecast x Lead-time x Maximum Factor
The difference in quantity between available units and maximum units is the reorder value, providing the inventory level is below the reorder point. When stock drops below the reorder point, and when P/O Preliminary Generation (ibis_po23) runs, a preliminary PO is generated to bring stock levels back to the maximum.
Note: The reorder point and the maximum values are stored in the Products (ibis_ici1) table. These values are updated on an on-going basis through the Purchasing, Forecast and Leadtime Recalculation (ibis_po25) process.
- If reviewed cyclically, maximums are calculated as:
- Classification Method - this method of calculating ROQ sub-classifies inventory items in decreasing order of annual sales volume; for example, 5% of the inventory that is maintained by the system may account for 30% of annual sales.
-
Classification codes are manually assigned to each product in the Products (ibis_ici1) table, or are automatically assigned by Class Code Report and Reset (ibis_im61) on the basis of dollar or hit demand. The assumption in both cases is the higher the demand, the higher the sales dollar volume. Products that have a high dollar or hit demand (in proportion to the total $ demand) are coded with a higher-class code.
- The P/O Forecast Calculation (ibis_po07) table maintains all the information required to calculate the forecast usage using Purchasing, Forecast and Leadtime Recalculation (ibis_po25).
- The ABC Classes (ibis_im01) table manages the 'Days (ROQ)' file used to calculate the reorder quantity and the purchasing criteria code that should be applied to the products in this class code.
- Purchasing, Forecast and Leadtime Recalculation (ibis_po25) calculates the forecast for a product and then, if the method of calculating the ROQ is C, the monthly forecast is reduced to a daily requirement and multiplied by the number of days, maintained for the product's class code in ABC Classes (ibis_im01). Normally products that generate the highest unit forecast have the lowest number of days used to recalculate the ROQ. The assumption is made that a product with high volume will be reordered more frequently.
-
Classification codes are manually assigned to each product in the Products (ibis_ici1) table, or are automatically assigned by Class Code Report and Reset (ibis_im61) on the basis of dollar or hit demand. The assumption in both cases is the higher the demand, the higher the sales dollar volume. Products that have a high dollar or hit demand (in proportion to the total $ demand) are coded with a higher-class code.
- Economic Order Quantity Method - The EOQ method of calculating ROQ utilizes an equation that calculates the optimum quantity to order; i.e. once the optimum reorder quantity has been calculated, it becomes a static amount. The theory behind the EOQ model supports the idea that each product has an optimal order size (the EOQ), which will result in minimum total annual costs. The strategy is to order the same amount each time an order is placed.
- The equation used to calculate the economic order quantity for products is:
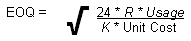
Where,
'R' = the cost to generate a purchase order,
'K' = the annual cost of carrying 1 unit in stock,
'Useage' = monthly usage calculated by P/O Forecast Calculation (ibis_po07)Note: The default 'R Factor' and the 'K Factor' are maintained in Company Control Initialization (ibis_cc00/Purchasing). The 'R Factor' can be also be applied on a supplier-by-supplier basis in P/O Suppliers (ibis_pos.po11). If the supplier's 'R Factor' is zero then the default 'R Factor' (from CC00) is used.
- The equation used to calculate the economic order quantity for products is:
- Manually set ROQ amount - the amount to be reordered is manually set for the product in the Porducts (ibis_ici1) table. This amount may only be reset manually.
- Safety Stock Factor - enter the factor used by the recalculation routines (ibis_po25/ibis_po27) to establish the safety stock (minimum) requirements for a product. The default value is 0.5.
- Safety stock is calculated as:
Minimum = Forecast x Lead Time x Safety Stock Factor
Note: The safety stock factor defaults to 0.5 because safety stock units are included in the reorder point and the line point calculations; however, the safety stock factor may be equal to any value greater than 0. The factor to use is dependent on the variances between actual versus estimated lead times and the forecast. As forecast and lead time values increase, the safety stock factor should increase also.
- Safety stock is calculated as:
For the functionality of each button on the search criteria/search results page, click here.
For the functionality of each button on the details page, click here.
